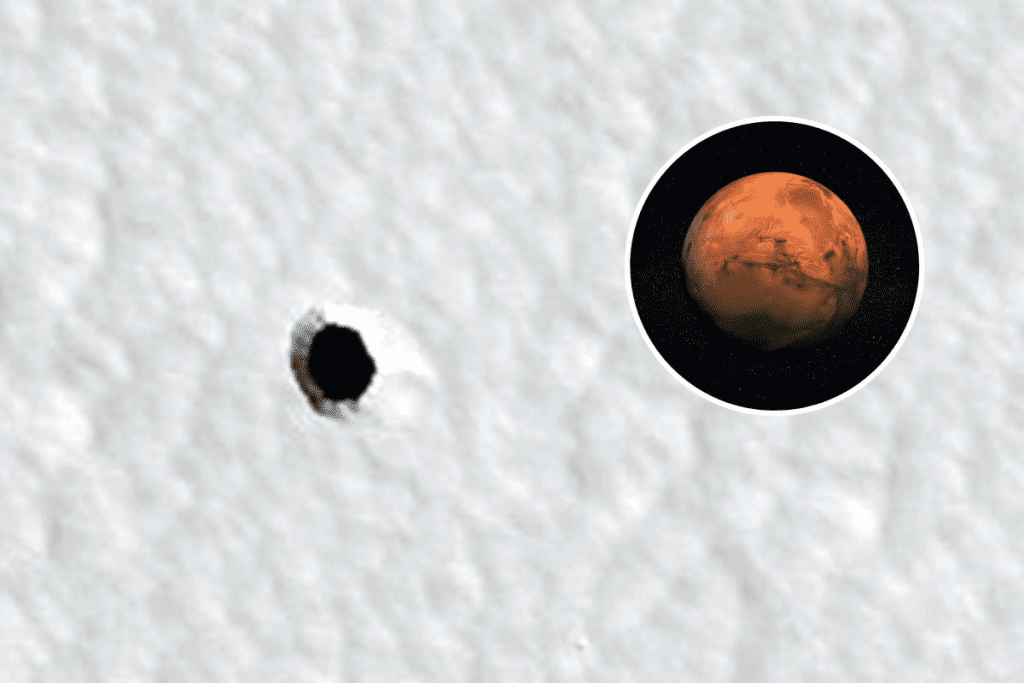
A newly discovered hole on Mars could provide crucial shelter for future explorers. Scientists are closely examining large underground lava tubes on the Red Planet, as they could offer protection against cosmic radiation, extreme temperature fluctuations, and the frequent dust storms that occur on Mars. These lava tubes, similar to those on the Moon, may become safe havens for astronauts embarking on long-term missions.
The Potential of Lava Tubes on Mars
Recent findings from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO), specifically the High-Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE) camera, have captured intriguing images of a large hole located in the Arsia Mons region on Mars. While the hole is only a few meters in diameter, it could potentially lead to a vast underground lava tube network, which might have been formed by ancient lava flows.
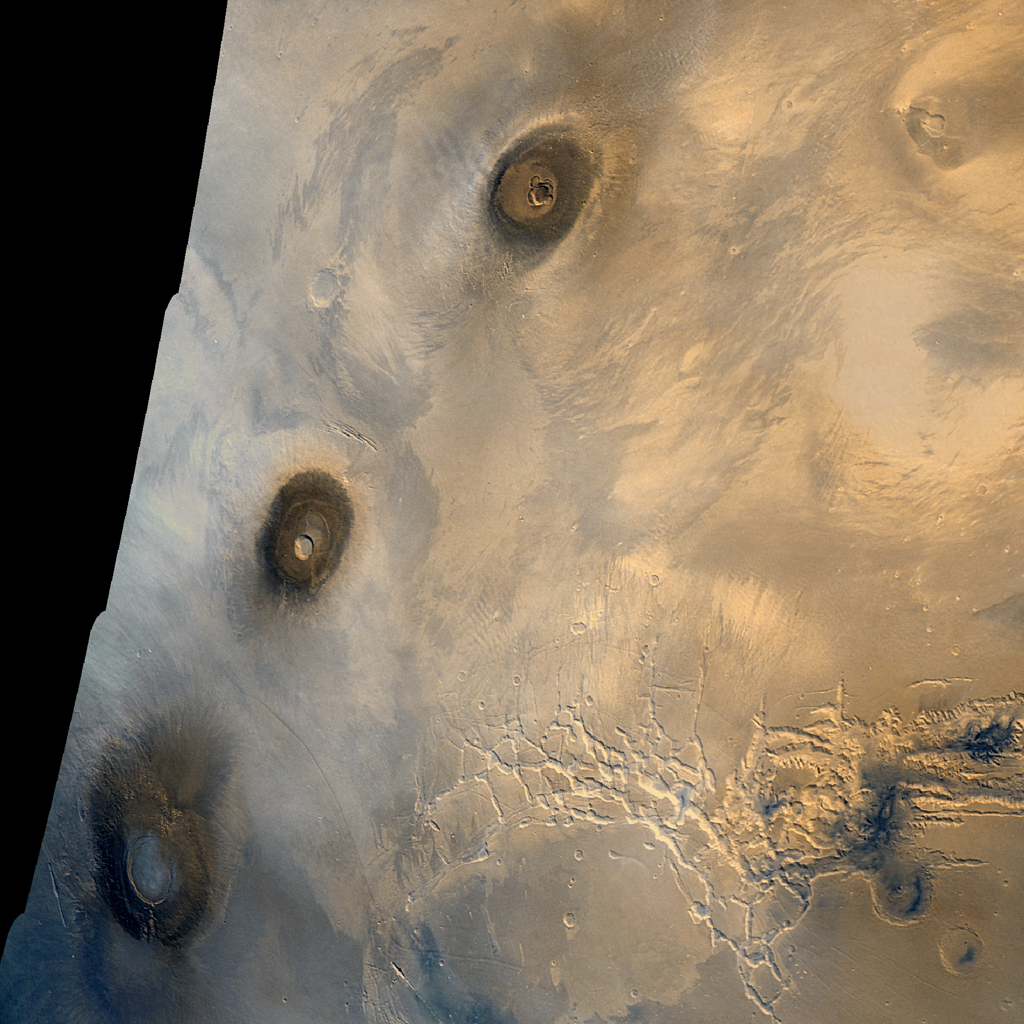
Arsia Mons, one of the three dormant volcanoes in the Tharsis Montes volcanic range, is a prime location for such features. The hole may be a “skylight,” which is a collapsed section of a lava tube, potentially providing a pathway into a large underground cavern. However, scientists caution that the hole could also be a simple cylindrical pit rather than a skylight.
The Significance of Lava Tubes
Lava tubes are hollow, cylindrical structures formed by flowing lava, and they have been found on Earth, the Moon, and Mars. On Earth, lava tubes can extend hundreds of meters deep, and similar structures are expected to exist on Mars due to the planet’s lower gravity. This lower gravity means that lava tubes may be larger and more extensive on Mars than on Earth, making them ideal candidates for shelter.
On the Moon, lava tubes have already captured the interest of scientists, with proposals to use these underground caverns as habitats for future lunar explorers. A 2021 proposal suggested building a “lunar ark” in the Moon’s lava tubes to store the DNA of millions of Earth species, essentially creating a modern-day global insurance policy. Similarly, Mars lava tubes could serve as protective shelters for astronauts, shielding them from the harsh Martian environment.

Exploring Lava Tubes on Mars
Understanding the geological formations on Mars, especially lava tubes, is crucial for planning future human missions. While most of the data on lava tubes comes from Earth-based studies and lunar research, scientists are increasingly confident that Mars has similar structures, waiting to be explored. In fact, past images have already revealed collapsed rilles, which are remnants of lava tubes that have caved in over time. These findings suggest that intact, structurally sound lava tubes may exist beneath the Martian surface.
Future Mars missions are likely to include robotic explorers tasked with identifying and mapping these underground caverns. These robots could help scientists assess whether the lava tubes are stable enough to serve as shelters for astronauts, protecting them from cosmic radiation, temperature extremes, and dust storms—challenges that currently pose significant risks to human habitation on Mars.
The Benefits of Lava Tubes for Mars Colonization
Lava tubes could offer a multitude of benefits for Mars colonization. These natural formations could shield astronauts from harmful cosmic radiation, which is one of the major challenges for long-term space missions. Without proper protection, exposure to radiation can cause severe health issues, including increased cancer risk. The thick walls of lava tubes provide a natural barrier that could absorb or block much of this radiation.
In addition, the temperature on Mars can fluctuate dramatically, ranging from -195°F (-125°C) at night to 70°F (20°C) during the day at the equator. Lava tubes, being underground, maintain a more stable temperature, providing a more habitable environment for astronauts. Dust storms on Mars, which can last for weeks, could also be mitigated by taking shelter inside these tubes, protecting equipment and human habitats from the damaging effects of the Martian winds.
Conclusion: A Promising Future for Mars Exploration
The discovery of large underground lava tubes on Mars, including the potential skylights in the Arsia Mons region, opens up exciting possibilities for future human missions to the Red Planet. These natural shelters could serve as safe havens for astronauts, providing protection against radiation, extreme temperatures, and dust storms. As robotic missions continue to explore Mars, it is likely that more lava tubes will be identified, bringing humanity one step closer to establishing a permanent presence on Mars.
By harnessing the protective qualities of Mars’ lava tubes, we can ensure a safer and more sustainable environment for future colonists. This discovery not only paves the way for future Mars exploration but also reinforces the importance of studying planetary geology to ensure the success of human space missions.